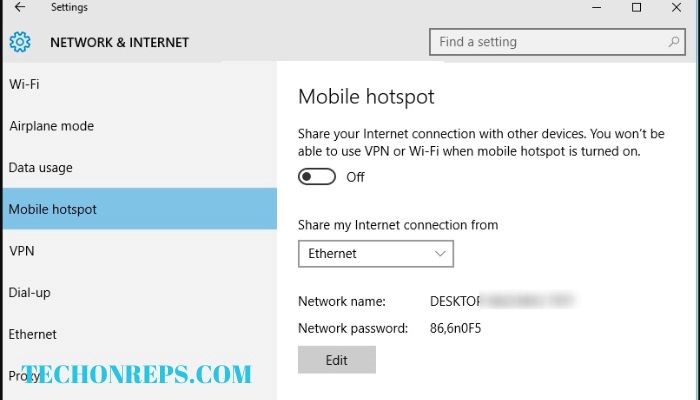
The Mystery of the Disconnected WiFi: Why Your Hotspot Can Connect to Remote Desktop But Not WiFi
We’ve all experienced the frustration of being unable to connect to WiFi despite having a strong signal. Whether it’s at home, in the office, or at a coffee shop, the inability to connect to the internet can be incredibly inconvenient and disruptive. It can prevent us from completing important tasks, accessing information, or simply enjoying our favorite online activities. In this article, we will explore why Your Hotspot Can Connect to Remote Desktop But Not WiFi and the common causes of disconnected WiFi and provide tips for troubleshooting and resolving these issues.
Understanding the Difference Between Remote Desktop and WiFi Connection
Before we delve into the causes of disconnected WiFi, it’s important to understand the difference between using a remote desktop connection and connecting to WiFi. A remote desktop connection allows you to access and control a computer from another device, such as a laptop or smartphone. This can be useful if you need to access files or programs on a different computer. However, it does not solve the underlying issue of disconnected WiFi. Even if you are able to establish a remote desktop connection, you may still experience slow or unreliable internet access if your WiFi connection is not working properly.
Common Causes of Disconnected WiFi
There are several common reasons why WiFi may not connect, ranging from simple user errors to more complex technical issues. One of the most common causes is an incorrect password. It’s easy to mistype or forget a password, especially if it’s a complex one. Another common cause is network congestion. If there are too many devices connected to the same network, it can slow down the connection or cause it to drop altogether. Additionally, hardware issues can also cause WiFi connectivity problems. This could be due to a faulty router, modem, or network adapter.
To identify these causes, you can start by double-checking the password you entered when trying to connect to WiFi. If it’s incorrect, simply enter the correct password and try again. If network congestion is the issue, you can try disconnecting some devices from the network or using a different WiFi channel to reduce interference. If you suspect a hardware issue, you can try restarting your router and modem, or contacting your internet service provider for assistance.
The Role of Network Drivers in WiFi Connectivity
Network drivers play a crucial role in WiFi connectivity. They are software programs that allow your computer to communicate with the network adapter, which is responsible for connecting to WiFi networks. Outdated or corrupted network drivers can cause WiFi issues, such as slow or intermittent connectivity, or the inability to connect at all. To resolve this issue, you can update your network drivers. This can usually be done through the device manager on your computer, or by visiting the manufacturer’s website and downloading the latest drivers for your specific network adapter.
The Impact of Outdated Firmware on WiFi Connection
Firmware is software that is embedded in a hardware device, such as a router or modem. It controls the device’s functionality and allows it to communicate with other devices on the network. Outdated firmware can cause connectivity issues, as it may not be compatible with the latest WiFi standards or security protocols. To update your firmware, you will need to access your router’s settings. This can usually be done by typing the router’s IP address into a web browser and entering the login credentials. Once you are logged in, look for a firmware update option and follow the instructions provided.
The Importance of Security Settings in WiFi Connectivity
Security settings play a crucial role in WiFi connectivity. They help protect your network from unauthorized access and ensure that your data is transmitted securely. However, incorrect security settings can also cause connectivity issues. There are several types of security settings, including WEP, WPA, and WPA2. WEP is the least secure option and should be avoided if possible. WPA and WPA2 are more secure and recommended for most users. To adjust your security settings, you will need to access your router’s settings and look for the wireless security or encryption option. From there, you can select the desired security type and enter a strong password.
The Effect of Interference on WiFi Signal Strength
Interference from other devices or networks can have a significant impact on WiFi signal strength. This can result in slow or unreliable internet access, or the inability to connect at all. Common sources of interference include cordless phones, microwave ovens, baby monitors, and neighboring WiFi networks. To minimize interference and improve signal strength, you can try moving your router away from these devices, or changing the channel on which your WiFi network operates. Most routers have a channel selection option in their settings, which allows you to choose the least congested channel in your area.
The Significance of Router Placement in WiFi Connection
Router placement is another important factor that can impact WiFi connectivity. The location of your router can affect the range and strength of your WiFi signal. Ideally, your router should be placed in a central location, away from walls, furniture, and other obstructions. It should also be elevated, such as on a shelf or mounted on a wall. This will help ensure that the WiFi signal is evenly distributed throughout your home or office. Additionally, you should avoid placing your router near other electronic devices or appliances that may cause interference.
Troubleshooting Tips for Disconnected WiFi
If you are experiencing disconnected WiFi, there are several troubleshooting tips you can try before seeking professional help. First, try resetting your router by unplugging it from the power source, waiting for a few seconds, and then plugging it back in. This can often resolve minor connectivity issues. If that doesn’t work, try updating your network drivers and firmware, as discussed earlier. You can also try connecting to a different WiFi network to see if the issue is specific to your network or device. If all else fails, you may need to contact your internet service provider for further assistance.
Conclusion:
Disconnected WiFi can be incredibly frustrating and inconvenient. However, by understanding the various factors that can impact WiFi connectivity, you can troubleshoot and resolve these issues effectively. Whether it’s an incorrect password, network congestion, outdated network drivers or firmware, incorrect security settings, interference, or router placement, there are steps you can take to improve your WiFi connection. By following the tips and suggestions provided in this article, you can ensure a reliable and stable WiFi connection for all your internet needs.